C++11 standard introduces new type of functions for C++ programming - lambda functions.
Lambda function is a anonymous (unnamed) function which you can write directly inline in the code.
Lambda function allows do some operations visible like a function without declaring it as a function (saving space and time).
C++ lambda function has following syntax:
[capture](arguments){body}
In point I we are initializing vector using C++11 initializer_list
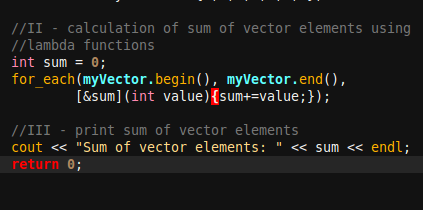
Point II is key point of our example. It demonstrate using lambda function (3rd argument of for_each function) together with with for_each algorithm of STL library in order to calculate sum of vector elements. In C++03 we had to define separate function (outside of our main function) in order to use it within some STL algorithm (ex. for_each as in this example). Thanks to lambda functions we can define such us such function without declaration - in place. It is definitely easier especially if we are going to use some small function once in our code.
In point III we are printing results of our calculations.
As you can see, lambda functions are very comfortable when you are going to use some small function only once withing your code (ex. calculate some sum).
Code of this example you can find in our GitHub account here: https://github.com/xmementoit/CppAdventureExamples/tree/master/cpp11/lambdaFunctions
Lambda function is a anonymous (unnamed) function which you can write directly inline in the code.
Lambda function allows do some operations visible like a function without declaring it as a function (saving space and time).
C++ lambda function has following syntax:
- capture - value which should be captured outside of body class
- arguments - list of arguments of function (the same syntax as for normal C++ functions)
- body - body of function - statements which should be exectued when function is invoked
In point I we are initializing vector using C++11 initializer_list
Point II is key point of our example. It demonstrate using lambda function (3rd argument of for_each function) together with with for_each algorithm of STL library in order to calculate sum of vector elements. In C++03 we had to define separate function (outside of our main function) in order to use it within some STL algorithm (ex. for_each as in this example). Thanks to lambda functions we can define such us such function without declaration - in place. It is definitely easier especially if we are going to use some small function once in our code.
In point III we are printing results of our calculations.
As you can see, lambda functions are very comfortable when you are going to use some small function only once withing your code (ex. calculate some sum).
Code of this example you can find in our GitHub account here: https://github.com/xmementoit/CppAdventureExamples/tree/master/cpp11/lambdaFunctions
Comments
Post a Comment